المواد القابلة لإعادة التدوير
أساسيات التقليل وإعادة الاستخدام
أكثر الطرق فعالية لتقليل النفايات هي عدم انتاجها من الأساس. فصناعة منتج جديد تُصدر غازات دفيئة تساهم في تغير المناخ وتتطلب الكثير من المواد والطاقة، حيث يجب استخراج المواد الخام من الأرض، ثم تصنيع المنتج ونقله إلى المكان الذي سيُباع فيه.
نتيجة لذلك، يعتبر التخفيف من النفايات وإعادة الاستخدام أكثر الطرق فعالية للحفاظ على الموارد الطبيعية وحماية البيئة وتوفير المال. تقوم وكالة حماية البيئة (EPA) بتوضيح طرق مختلفة للتقليل وإعادة الاستخدام كما يلي:


فوائد التقليل وإعادة الاستخدام
يقلل من انبعاثات الغازات الدفيئة التي تساهم في تغير المناخ العالمي.
يمنع التلوث الناجم عن تقليل الحاجة لاستخراج المواد الخام الجديدة.
يوفر الطاقة.
يساعد في الحفاظ على البيئة للأجيال القادمة.
يقلل من كمية النفايات التي يجب إعادة تدويرها أو إرسالها إلى المدافن أو محارق النفايات.
يسمح باستخدام المنتجات إلى أقصى حد.
يوفر المال.


أفكار حول كيفية التقليل وإعادة الاستخدام
فكر في البيئة قبل أن تتسوق: قلل من انبعاثات غازات الدفيئة المرتبطة بالتسوق عن طريق التفكير بالبيئة عند الشراء.
قلل من هدر الطعام من خلال التسوق الذكي، وشراء ما تحتاجه فقط، وتحويل بقايا الطعام إلى سماد، والتبرع بالطعام غير المستخدم للبنوك الغذائية أو الجمعيات.
أعد استخدام أو إعادة تدوير العناصر مثل الملابس القديمة، وأكياس التسوق القماشية، والحاويات لمنع النفايات.
اشترِ العناصر المستعملة لتقليل النفايات وكذلك الانبعاثات الناتجة عن إنتاج المواد الجديدة أو التخلص منها في مدافن النفايات. تبرع بالملابس غير المستخدمة، والإلكترونيات، ومواد البناء لضمان أن يتمكن الآخرون من إعادة استخدامها أيضًا!
اشترِ المنتجات المصنوعة من محتوى معاد تدويره. تحقق من العلامات لمعرفة ما إذا كان المنتج أو عبواته مصنوعة من مواد معاد تدويرها.
اعرف ما الذي يجب رميه: اعرف أي العناصر التي تجمعها برامج إعادة التدوير المحلية لديك، وشجع أسرتك على إعادة التدوير بشكل صحيح وأكثر.
تعلم المزيد عن ما يمكنك فعله في المنزل، في المدرسة، في العمل، وفي مجتمعك!
قم بصيانة وإصلاح المنتجات، مثل الملابس والأجهزة، حتى لا تضطر إلى التخلص منها واستبدالها بشكل متكرر.
استعِر، استأجر أو شارك العناصر التي تُستخدم بشكل غير متكرر، مثل زينة الحفلات، أو الأدوات.

أساسيات إعادة التدوير وفوائدها
إعادة التدوير هي ممارسة جمع ومعالجة مواد النفايات لإنشاء منتجات جديدة. تعود فوائد إعادة التدوير على المجتمع والاقتصاد والبيئة. يجب إعادة التدوير المنتجات التي لا يمكن تقليصها أو إعادة استخدامها. يجب الالتزام بهرم إدارة النفايات، الذي يصنف أنظمة إدارة النفايات من الأكثر استدامة إلى الأقل. يولي هذا الهرم الأولوية لتقليل النفايات، ثم إعادة استخدامها، وأخيرًا إعادة التدوير.
نظرة عامة على نظام إعادة التدوير
تتكون عملية إعادة التدوير من ثلاث خطوات يتم تكرارها مرارًا وتكرارًا. حيث يخلق حلقة مستمرة تمثلها الرموز الشائعة لأسهم إعادة التدوير. توضح وكالة حماية البيئة (EPA) الخطوات الثلاث لعملية إعادة التدوير كما يلي:
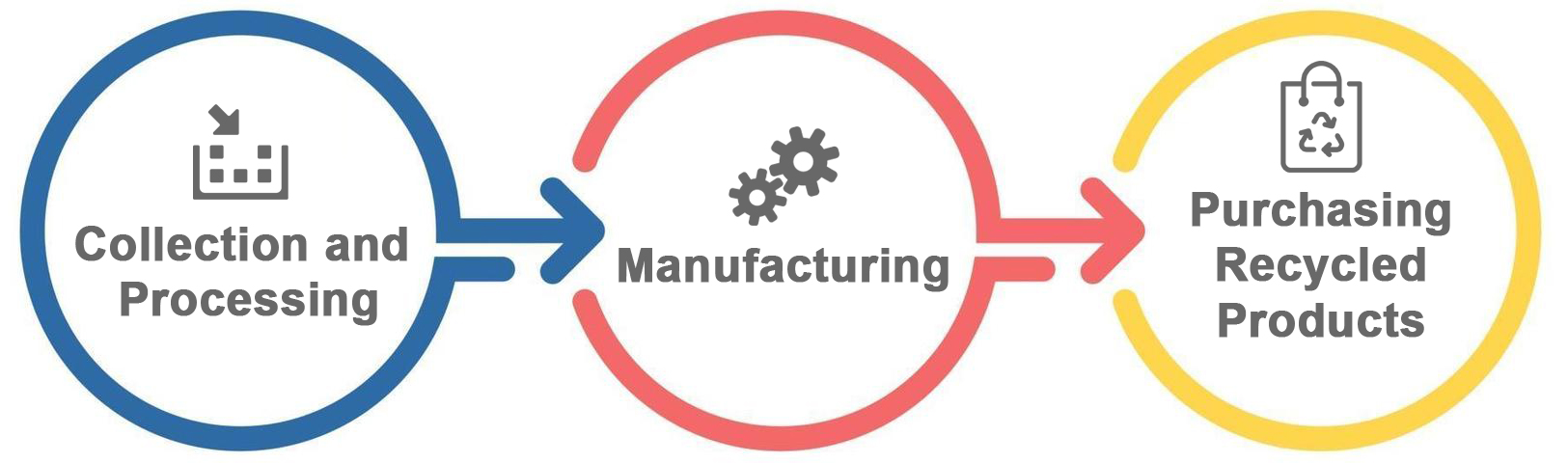
الخطوة 1: الجمع والمعالجة
تولد الشركات والمستهلكون المواد القابلة لإعادة التدوير التي يتم فصلها في المصدر ثم جمعها عادةً بواسطة مقدمي خدمات اعادة التدوير. هناك عدة طرق لجمع المواد القابلة لإعادة التدوير، بما في ذلك جمع النفايات من الأرصفة، ومراكز التوزيع، وبنوك إعادة التدوير.
بعد الجمع، يتم إرسال المواد القابلة لإعادة التدوير إلى منشأة استرداد لتُنظف وتُعالج إلى مواد يمكن استخدامها في التصنيع. يتم شراء وبيع المواد القابلة لإعادة التدوير مثل المواد الخام، وتختلف الأسعار بناءً على العرض والطلب في السوق.

الخطوة 2: التصنيع
بعد المعالجة، يتم تحويل المواد القابلة لإعادة التدوير إلى منتجات جديدة في مصنع إعادة التدوير أو منشأة مشابهة. يتم تصنيع المزيد والمزيد من المنتجات اليوم باستخدام محتوى معاد تدويره.
يتم أيضًا استخدام المواد المعاد تدويرها بطرق جديدة مثل الزجاج المستعاد في الأسفلت لتعبيد الطرق أو البلاستيك المستعاد في السجاد والمقاعد في الحدائق.

الخطوة 3: شراء منتجات جديدة مصنوعة من مواد معاد تدويرها
أنت تساعد في إغلاق حلقة إعادة التدوير من خلال شراء منتجات جديدة مصنوعة من مواد معاد تدويرها. هناك الآلاف من المنتجات التي تحتوي على محتوى معاد تدويره. عندما تذهب للتسوق، ابحث عن ما يلي:
– المنتجات التي يمكن إعادة تدويرها بسهولة
– المنتجات التي تحتوي على مواد معاد تدويرها


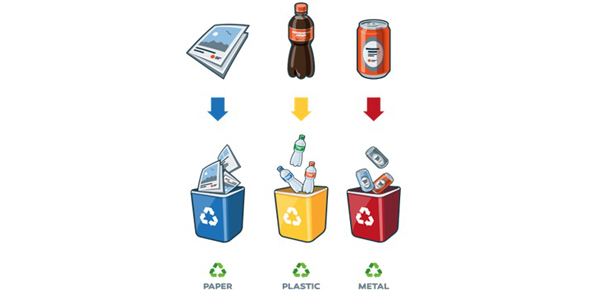
الفصل من المصدر
الفصل من المصدر هو الخطوة الأولى والأكثر أهمية في إعادة التدوير واستعادة قيمة النفايات. كما أنها خطوة هامة في إدارة النفايات في الموقع بشكل سلس وفعال من حيث التكلفة. يتم توليد النفايات في أي منشأة من مصادر متعددة وتأتي في أنواع مختلفة من المواد مثل الزجاج، والورق، والبلاستيك، وبقايا الطعام، وغيرها. عندما تختلط النفايات في صناديق النفايات، يتطلب الأمر جهودًا إضافية لفرزها لاحقًا لاستعادة المواد لإعادة التدوير. بالإضافة إلى ذلك، قد تتلوث بعض المواد ويصبح من الصعب إعادة تدويرها، مثلا عندما يتلوث البلاستيك ببقايا الطعام أو أنواع أخرى من البلاستيك والمخلفات، فقد يتم إعادة تدويرها إلى بلاستيك منخفض القيمة أو يصبح من المكلف جدًا فرزها وتنظيفها مما يؤدي إلى عملية إعادة تدوير غير مربحة. يشير الفصل عند المصدر إلى ضمان عدم اختلاط النفايات من البداية.

يمكن أن يتم الفصل من المصدر من خلال استراتيجيات متنوعة. على سبيل المثال، يمكن اختيار الفصل العميق بوضع صناديق مخصصة لإعادة التدوير للورق، والمعادن، والزجاج، والبلاستيك، وبقايا الطعام، وغيرها. وهذه هي إحدى استراتيجيات الفصل المتقدمة عند المصدر التي تعزز من فرص استعادة قيمة النفايات بشكل أكبر. يمكن أن تركز استراتيجيات أبسط على فصل النفايات الغذائية والعضوية في نوع واحد من الصناديق (المعروفة بالنفايات الرطبة) وكل شيء آخر في صندوق منفصل (المعروف بالنفايات الجافة). تعتمد هذه الاستراتيجية على حقيقة أنه من الأسهل للمُعيدين تدوير النفايات الجافة مثل المعادن والبلاستيك والورق بشكل منفصل عن النفايات الرطبة (النفايات العضوية). هذه الاستراتيجية أسهل في التنفيذ ولكنها تستعيد أقل قيمة وكمية من النفايات. عادة ما يتم تمييز صناديق الفرز من خلال علامات وألوان، وقد يتطلب الأمر أحيانًا زيادة الوعي بين موظفي المنشأة. وأحيانًا، يحتاج عملاؤك إلى التواصل بشأن الهدف من الفصل وكيفية تنفيذه.
استراتيجية أخرى هي التركيز على الفصل عند المصدر في جزء معين من المنشأة أو لنوع معين. على سبيل المثال، يمكن وضع صندوق خاص لنفايات الورق بالقرب من مكاتب الموظفين أو بالقرب من الطابعات. و على سبيل المثال ايضا، وضع صندوق لأكواب القهوة بالقرب من الأماكن التي تُباع فيها القهوة في المنشأة.
بجانب منحك الفرصة لبيع المواد القابلة لإعادة التدوير أو على الأقل الحصول على خصم من مزود الخدمة، هناك العديد من الفوائد الأخرى. يشير الفصل من المصدر إلى أن مؤسستك تهتم بالبيئة وتحاول زيادة فرص إعادة التدوير. بالإضافة إلى ذلك، فإنه يؤدي إلى تقليل الزحام في جمع وإدارة النفايات في منشأتك. على سبيل المثال، إذا قمت بفصل نفايات الطعام عن الأنواع الأخرى من النفايات، يمكنك التركيز على إزالة نفايات الطعام من الصناديق بشكل أكثر تكرارًا، مما يؤدي إلى بيئة أكثر نظافة وأقل جهدًا في إفراغ صناديق النفايات الجافة. كما أن الفصل يسمح لك بضبط حجم الصناديق وفقًا لنوع النفايات المتولدة في منطقة معينة (على سبيل المثال، صناديق أكبر للنفايات الغذائية بالقرب من مناطق تناول الطعام في المول). الفصل عند المصدر هو الخطوة الأكثر أهمية في صناعة إعادة التدوير الناجحة.

كيف يمكنني إعادة تدوير المواد القابلة لإعادة التدوير؟
قرارك بإعادة تدوير العناصر هو الخطوة الأولى فقط. من المهم أيضًا التأكد من أن العناصر يتم إعادة تدويرها بشكل صحيح. فيما يلي بعض المواد القابلة لإعادة التدوير الشائعة والمعلومات المتعلقة بإعادة تدويرها.
للحصول على نصائح عامة حول كيفية إعادة التدوير بشكل صحيح، يمكنك زيارة صفحة “إعادة التدوير 101” على موقع وكالة حماية البيئة (EPA).
الورق / الكرتون
يشكل الورق نسبة كبيرة من النفايات الصلبة البلدية (النفايات) التي يتم توليدها كل عام. يتم استخدام الورق المستعاد لصنع منتجات ورقية جديدة، مما يوفر الأشجار والموارد الطبيعية الأخرى. ابحث عن المنتجات المصنوعة من الورق المعاد تدويره عندما تتسوق. أفضل من ذلك، فكر في ما إذا كنت بحاجة حقًا للطباعة في المقام الأول.
أمثلة على العناصر الورقية / الكرتونية التي يمكن إعادة تدويرها:
– الصحف
– المجلات والكتب
– صناديق البيتزا إذا لم تكن تحتوي على دهون
– البريد والمغلفات
– حاويات وعلب الورق إذا لم تكن ملوثة
البلاستك
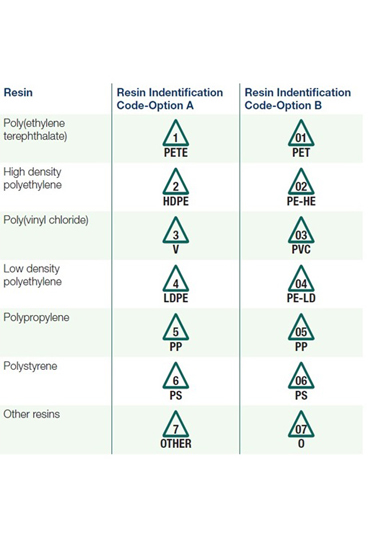
كن على علم بأن بعض أنواع البلاستيك لا يتم قبولها في برامج إعادة التدوير. عند الإمكان، اشترِ منتجات مصنوعة من مواد قابلة لإعادة التدوير أو من مواد بلاستيكية معاد تدويرها.
تم إنشاء هذه الرموز الموجودة في أسفل زجاجات البلاستيك والحاويات لتحديد نوع البلاستيك المستخدم في صنع الحاوية. يمكن أن يساعدك هذا في تحديد ما إذا كان العنصر قابلًا لإعادة التدوير من قبل مزود الخدمة الخاص بك.
الرقم الموجود داخل مثلث يشبه إلى حد كبير رمز إعادة التدوير. ومع ذلك، فإن هذا الرمز لا يعني بالضرورة أنه يمكن جمعه لإعادة التدوير في منطقتك.

الألمنيوم
يمكن إعادة تدوير علب الألمنيوم والألمنيوم المستخدم (مثل ورق الألمنيوم).

المعادن
تتمتع المعادن الحديدية (الحديد والفولاذ) بمعدل إعادة تدوير مرتفع للغاية.

الزجاج
يمكن إعادة تدوير الزجاج، وخاصة الحاويات الزجاجية للطعام والمشروبات، مرارًا وتكرارًا.

الطعام
عمومًا، لا يمكن إعادة تدوير الطعام، لكن بعض المواد الغذائية قد تُعاد تدويرها أو تُستعاد (upcycled). ومع ذلك، فإن التخلص من الطعام في القمامة ليس الخيار الأفضل لإدارة النفايات. يُوصى بتقليل هدر الطعام عن طريق شراء ما تحتاجه فقط وتناول بقايا الطعام. التحويل إلى سماد هو طريقة صديقة للبيئة للتخلص من نفايات الطعام أيضًا.

الزيت المستخدم
لا تقم أبدًا بصب زيت المحرك المستخدم في المجاري، يمكن للزيت المستخدم من تغيير زيت واحد أن يلوث مليون جالون من المياه العذبة. من خلال إعادة تدوير الزيت المستخدم، تساعد في الحفاظ على نظافة مصدر المياه لدينا. بالإضافة إلى ذلك، يستغرق الأمر جالون واحد من الزيت المستخدم لإنتاج 2.5 كوارت من زيت المحرك الجديد مقارنة بـ 42 جالونًا من النفط الخام. تقبل العديد من الشركات المتخصصة الزيت لإعادة تدويره.

الإطارات
تلتزم معظم المرائب بقبول وإعادة تدوير إطاراتك المستخدمة من خلال مقدمي خدمات متخصصين عندما تقوم بتركيب إطارات جديدة.

الإلكترونيات
حوالي 38.5٪ من الإلكترونيات يمكن إعادة تدويرها. لا يمكن إعادة تدوير الإلكترونيات من الأرصفة، ولكن يمكن تسليمها في مواقع جمع محددة. يوفر مقدمو الخدمة المتخصصون العديد من الخيارات للتبرع أو إعادة تدوير الإلكترونيات، بما في ذلك الهواتف المحمولة، وأجهزة الكمبيوتر، وأجهزة التلفاز.


منع إهدار الطعام
يجب على معظم الناس أن يدركوا مقدار الطعام الذي يرمونه كل يوم من بقايا الطعام غير المأكولة إلى الفواكه والخضروات المتعفنة إلى أجزاء من الفواكه والخضروات التي يمكن تناولها أو إعادة استخدامها. يعد منع هدر الطعام من أسهل وأقوى الإجراءات التي يمكنك اتخاذها لتوفير المال وتقليل بصمتك البيئية من خلال تقليل انبعاثات الغازات الدفيئة والحفاظ على الموارد الطبيعية.
فوائد منع هدر الطعام:
– توفير المال: من خلال شراء ما تحتاجه فقط، وتناول ما تشتريه، وتجنب رمي الطعام.
– تقليل بصمتك البيئية وبصمتك على تغير المناخ، وذلك من خلال:
– الحفاظ على الموارد والطاقة عندما يُهدر الطعام، يتم أيضًا هدر الأرض والمياه والطاقة والموارد الأخرى التي تم استخدامها في إنتاج الطعام ومعالجته ونقله وتحضيره وتخزينه والتخلص منه.
– تقليل انبعاثات غازات الدفيئة (GHG: أكثر من 85% من انبعاثات الغازات الدفيئة الناتجة عن النفايات الغذائية المدفونة في المكبات تأتي من الأنشطة التي تحدث قبل دخول الطعام إلى المكب، مثل الإنتاج والنقل والمعالجة وتوزيع الطعام. بالإضافة إلى ذلك، عندما يتحلل الطعام في المكب، يتم إطلاق الميثان، وهو غاز دفيئة قوي.

بناء خطة إدارة النفايات الخاصة بمنشأتك
إحدى أهم الخطوات نحو ممارسات فعّالة في تقليل النفايات وإعادة استخدامها وإعادة التدوير هي بناء خطة لإدارة النفايات. لمزيد من المعلومات حول ذلك، يرجى الرجوع إلى قسم خطة وإرشادات إدارة النفايات.


بنوك إعادة التدوير
يتم التعاون مع أمانة عمان الكبرى (GAM) لتنفيذ مشروع تجريبي لإنشاء “بنك إعادة التدوير” في عمان كحل جديد ومبتكر يهدف إلى تشجيع ممارسات “الفصل من المصدر” واختبار نماذج أعمال جديدة لإعادة التدوير في المناطق الحضرية، من حيث المتطلبات المقترحة، والأحجام والكميات الفعلية. سيتمكن الأفراد والكيانات وجامعي النفايات من تسليم النفايات القابلة لإعادة التدوير مباشرة إلى بنك إعادة التدوير، والحصول على مكافآت أيضًا.

التعاقد مع مزودي خدمات إعادة التدوير
في رحلة التحول لمرافق الأعمال التي تولد النفايات نحو تقليل النفايات وإعادة استخدامها وإعادة تدويرها، تتطلب العديد من التدابير والخطوات دعم مقدمي خدمات اعادة التدوير للتأكد من فعالية تعاون الطرفين. قد تكون خدمات إدارة النفايات وإعادة التدوير متنوعة وأحيانًا صعبة التعريف.
من الأهمية القصوى:
– اختيار مقدمي الخدمات المرخصين المناسبين.
– اختيار الحزمة المناسبة من الخدمات.
– تطوير اتفاقيات ملائمة وعادلة لخدمات مقدمي الخدمة.
تم تطوير دليل يحتوي على قائمة بمقدمي الخدمات في عمان من قبل مشروع “إعادة التدوير في الأردن” التابع للوكالة الأمريكية للتنمية الدولية (USAID). يتم أيضًا تحديد الخدمات التي يقدمها كل مزود خدمة بالإضافة إلى نطاق الخدمات في الدليل.
يسهل هذا البحث عن مقدمي الخدمات الأكثر ملائمة. كما يمكن أن يوفر الدليل خيارات لإعادة تدوير النفايات، حسب نوع النفايات، من خلال مزودي الخدمات العاملين في منطقة المرفق التجاري. لا يمثل الدليل بالضرورة جميع مقدمي الخدمات في السوق، بل أولئك الذين تم تحديدهم من قبل مشروع “إعادة التدوير في الأردن”.
علاوة على ذلك، فإن من مسؤولية مُنتِج النفايات التحقق من مقدمي الخدمات المرخصين الذين يمكنهم تلبية توقعاته من حيث الأداء وفقًا لأفضل الاتفاقيات . يرجى الرجوع إلى دليل مقدمي الخدمات لمزيد من المعلومات.

لمزيد من المعلومات حول المواد القابلة لإعادة التدوير والخيارات المتاحة، نشجعك على زيارة صفحة إعادة التدوير في وكالة حماية البيئة (EPA) هنا.